
Written by: Kevin Owens
Edited by: Pierce Young
What deer eat:
White-tailed deer are opportunistic foragers that eat a variety of vegetation depending on what is available to them throughout the year, including forbs (herbaceous broad-leaved plants), browse (twigs, vines, and leaves of woody plants), grasses (mainly young early growth stage cereal grains and cool-season annuals), sedges, and hard and soft mast (acorns and berries). It has been documented that deer consume over 400 different species of plants in the Southeastern part of the U.S. Changes in their diet mainly depend on forage abundance and seasonal changes. Browse and forbs are the most important forages providing over 80% of the diet (Browse = 45-65%; Forbs = 20-40%) in all seasons except Fall when mast is available.
(Click this link to read a deer forage guide booklet)
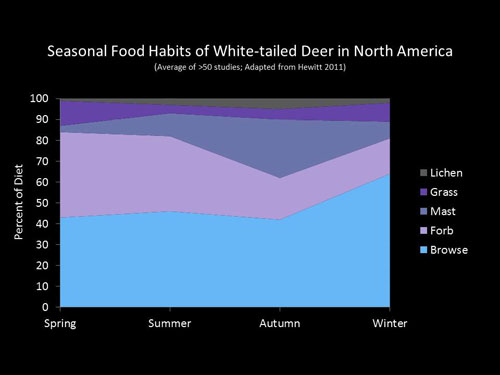
Source of graph: MSU Deer Lab
Why?
Forbs (Broadleaf Herbaceous Plants)
Examples: clover, ragweed, goldenrod
Why? Forbs are typically high in protein and digestible energy; especially in Spring and Summer when deer are recovering from Winter, bucks are growing antlers, and does are preparing for fawning.
Browse (Woody Plants)
Examples: greenbrier, blackberry, dewberry, trumpet-creeper
Why? Browse is available year-round; especially important during Fall and Winter when green plants are scarce. It provides fiber, moderate energy, and minerals.
Mast (Fruits and Nuts)
Hard mast examples: acorns
Soft mast examples: berries, persimmons
Why? Hard mast is rich in fats and carbohydrates, while soft mast is rich in fats and vitamins.
Grasses and Sedges
Examples: young early stages of: cereal grains (wheat, oats, rye), switchgrass, bluestem, gamagrass, nutsedges
Why? These are typically low in nutritional value for deer and are eaten more when increased quantity of foods are needed such as during winter, and higher-quality foods are more scarce. Deer only prefer these plants when they are young, tender, and more palatable.
Photo by Steve Gulledge
How to promote more plants deer prefer:
Habitat management techniques that aim to increase sunlight exposure to promote plant growth and improve wildlife habitat and deer browse.
- Timber Thinning - involves selectively removing trees to let more light reach the forest floor, encouraging understory growth.
- Patch Clearcutting - creates open, sunny areas beneficial for sun-loving species, often followed by replanting or natural regeneration.
- Edge management - enhances biodiversity by creating gradual transitions between habitats that receive varying amounts of sunlight.
- Brush management - removes invasive or overgrown mid-story trees that block light from reaching native ground plants.
- Controlled burns - reduce dense vegetation and leaf litter, reset plant succession, increasing light penetration and recycling nutrients back into the soil.
- Food plots - planted to provide extra nutrition during times when native vegetation is scarce or of low-quality, and typically include plants that are palatable to deer and/or provide high protein
For more information on the white-tailed deer diet and habitat management techniques please visit
www.mdwfp.com/wildlife-management-info