
Written by: Kevin Owens
Edited by: Pierce Young
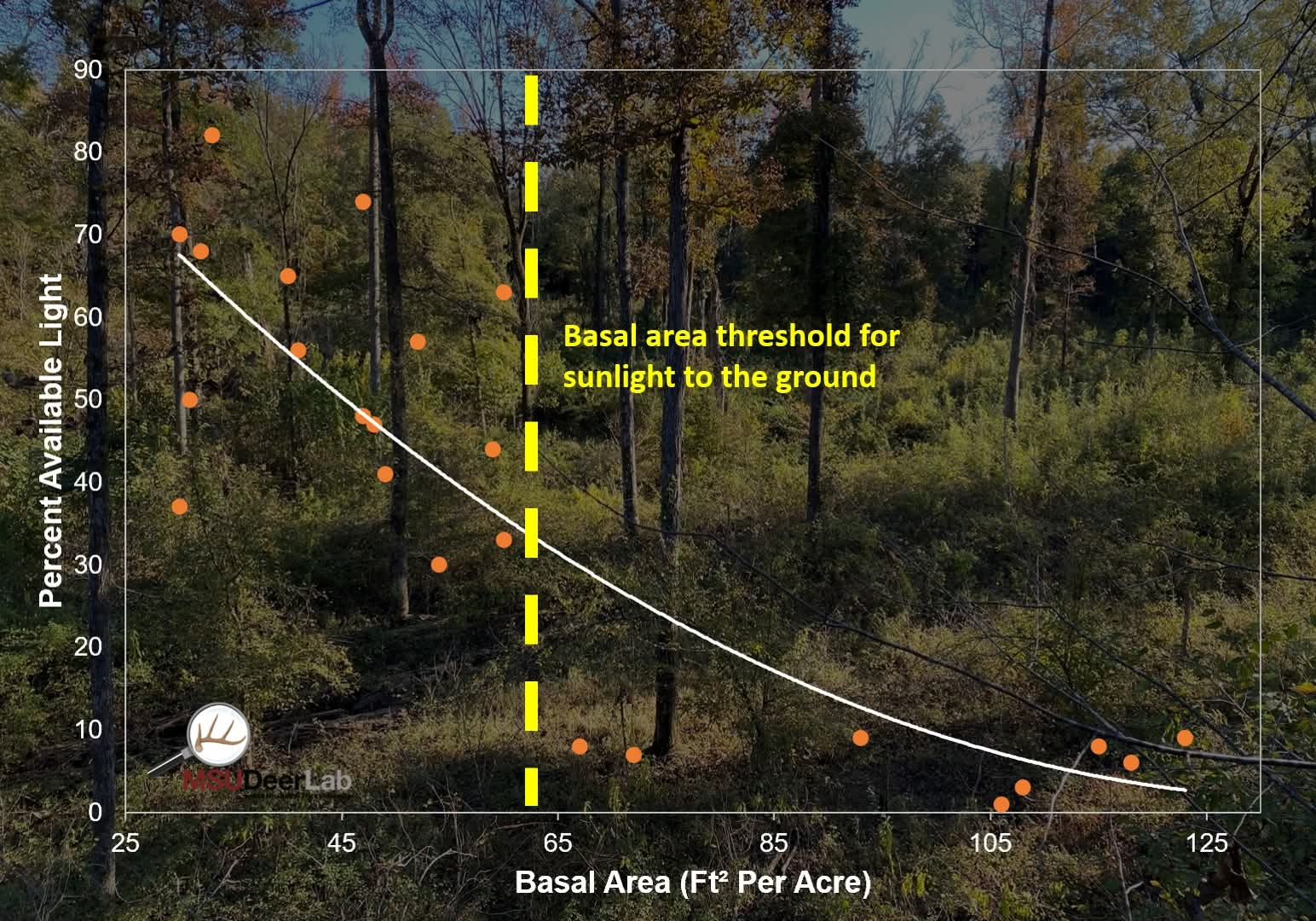
Managing wildlife habitats often centers on manipulating the environment to optimize one critical factor—sunlight. Sunlight is a fundamental driver of plant growth, directly influencing which plant species can thrive in a given area. Habitat management practices that enhance sunlight exposure at ground level typically involve creating open spaces or modifying vegetative structures. These actions help support early successional species and promote diverse, productive vegetation communities that provide essential food and cover for wildlife.

Sunlight plays a vital role in plant growth through photosynthesis, the process plants use to convert sunlight into energy. Increased sunlight exposure generally results in greater plant productivity. When sunlight reaches the ground—where many game species forage and seek cover—it boosts the growth of grasses, forbs, shrubs, and saplings, all of which serve as key food and shelter resources for wildlife.
Different plant species have varying sunlight requirements. Many of the highest-quality plants for wildlife thrive in full sun, while a few others, such as ferns (which generally have low wildlife value), are better adapted to shaded conditions. This variation in light tolerance shapes plant community composition, influences species diversity, and directly affects wildlife habitat by determining the availability of forage, nesting sites, and cover.
Examples of forage production for white-tailed deer based on forest management practices:
- Closed-canopy forest: 50–100 lbs per acre per year
- Thinned or select-cut forest: 400–600 lbs per acre per year
- Clearcut opening: 800–1,200 lbs per acre per year
Habitat management techniques that aim to increase sunlight exposure to promote plant growth and improve wildlife habitat:
- Commercial Thinning - Selective removal of trees through a timber harvest operation to increase sunlight penetration and stimulate understory vegetation growth.
- Commercial Clearcutting - Removal of all trees in a designated area, creating full-sun conditions ideal for sun-loving plants. This technique is often followed by natural regeneration or replanting.
- Edge Management - Enhances biodiversity by creating gradual transitions between habitats that receive varying degrees of sunlight, supporting a range of plant and animal species.
- Brush Management - Involves removing invasive or overly dense shrubs in the understory or midstory that block sunlight from reaching native ground-level plants.
- Non-commercial Timber Stand Improvement (TSI) - Uses methods such as chemical injection or chainsaw felling to selectively remove trees and improve light conditions in the forest understory without the need for commercial harvest.
- Controlled Burns (Prescribed Fire) - Uses fire to reduce accumulated leaf litter and dense understory vegetation, resetting plant succession, thereby increasing sunlight penetration and recycling nutrients back into the soil to stimulate new growth.
For more information on wildlife management visit