The following rules were promulgated by the Mississippi Commission on Wildlife, Fisheries, and Parks and the Mississippi Department of Agriculture and Commerce to minimize the introduction and movement of aquatic nuisance species.
Fisheries Rule 1.1 Prohibited Species: Possession of live Walking Catfish, PIranhas, Snakeheads and Swamp Eels is prohibited.
Fisheries Rule 1.3 Regulations Regarding Sport Fishing: Anglers using dip or landing nets, cast nets, boat mounted scoops, wire baskets, minnow seines, and minnow traps to capture shad and minnows and fishing in the spillways of Ross Barnett and Okatibbee Reservoirs, Grenada, Enid, Sardis, Arkabutla, Columbus, Aberdeen, and Bluff (Noxubee County) Lakes must immediately place their legal catch on ice or in a dry container.
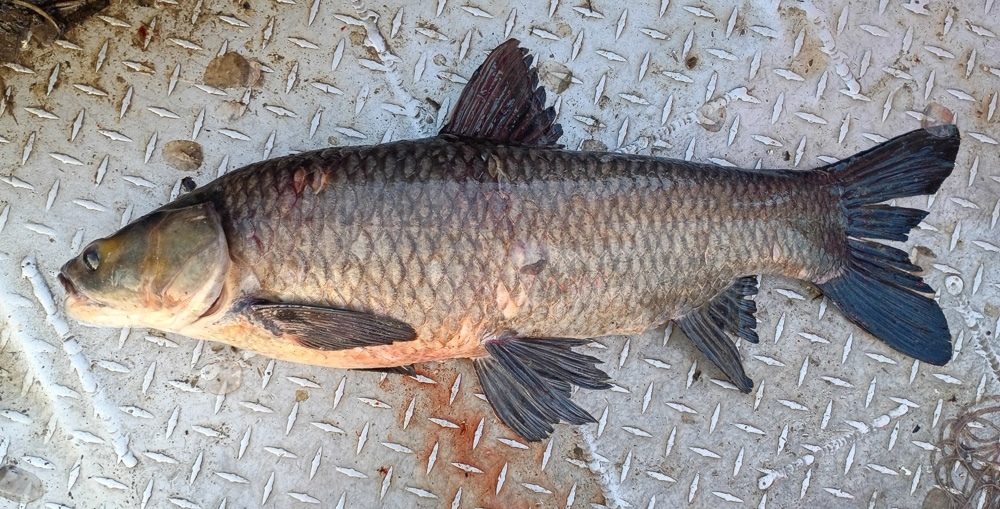
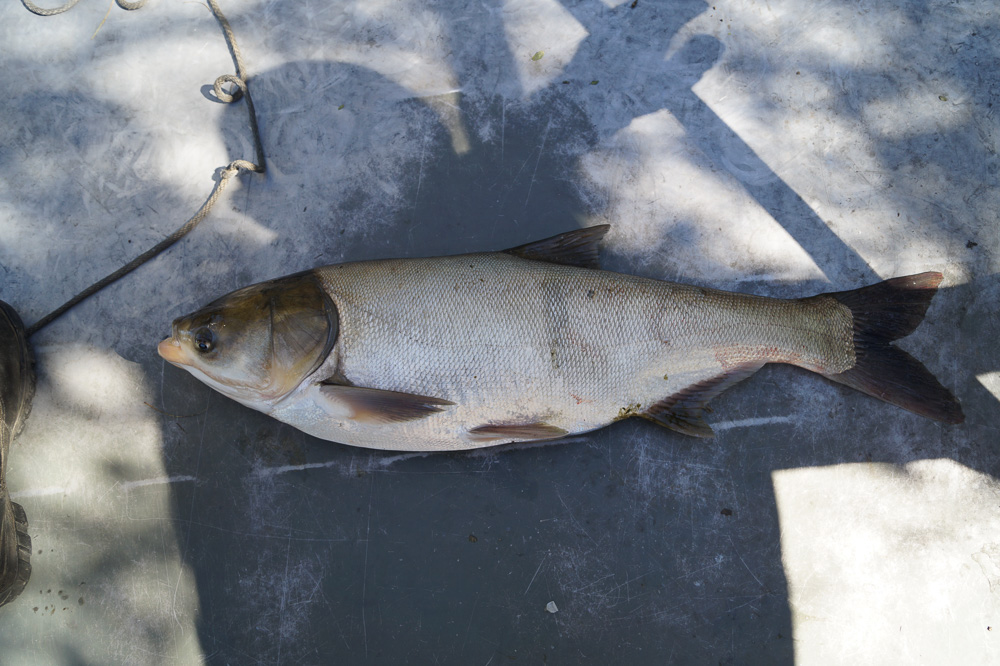
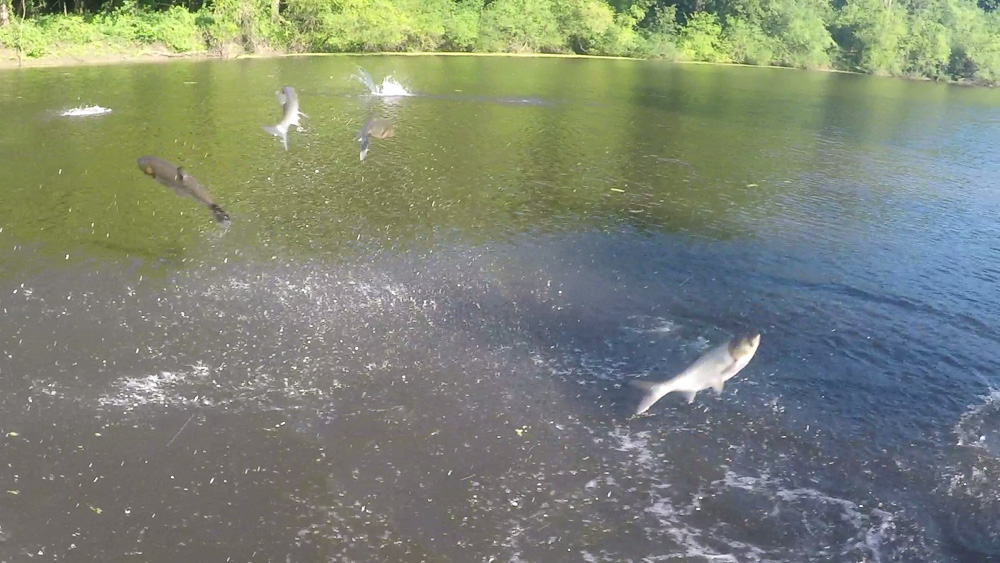
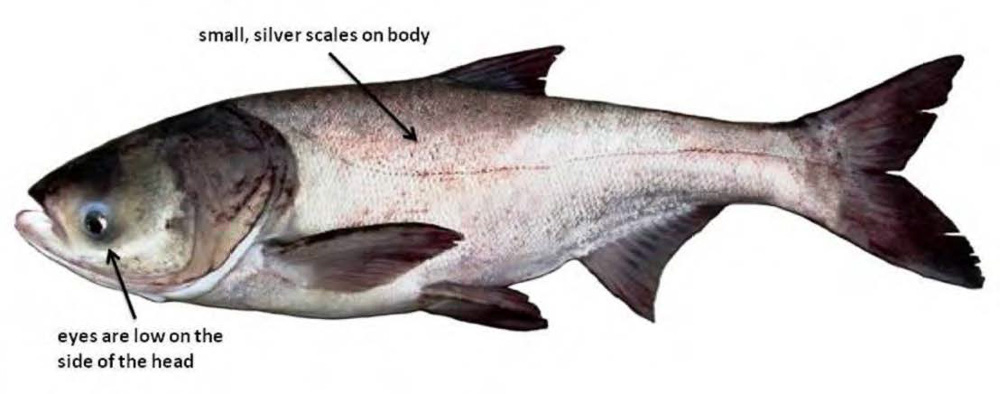
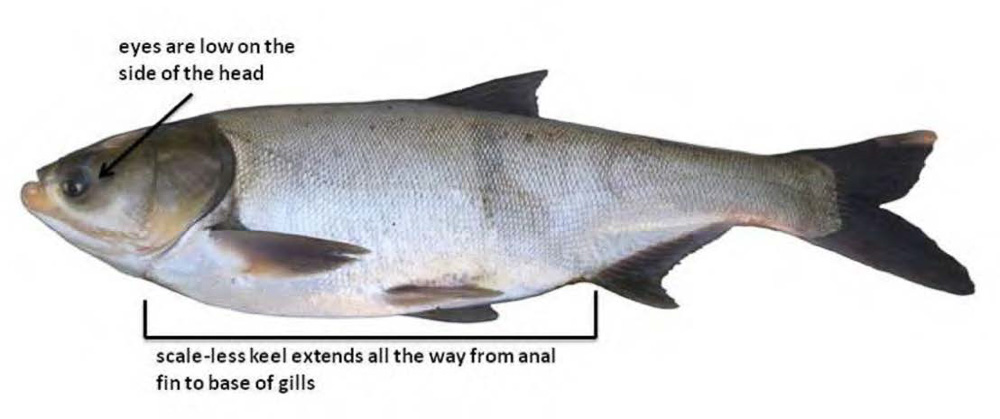
Fisheries Rule 3.1 Commercial Fishing Regulations: Only DEAD nonnative fish such as Invasive Carp can be used as bait, and only DEAD nonnative fish can be transported out-of-state for sale.
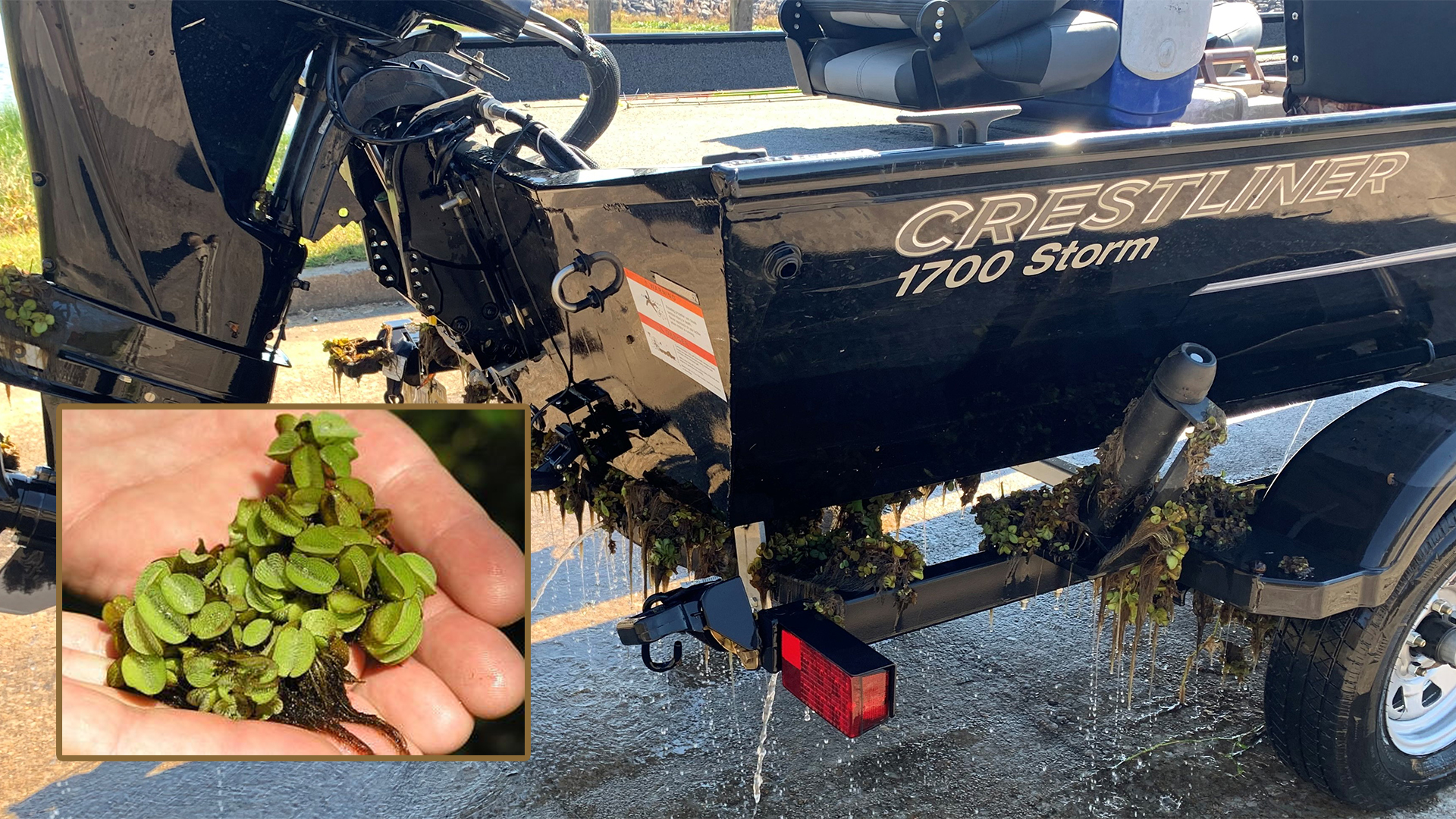
Additional prohibited species are listed in the Guidelines for Aquaculture Activities Rule.